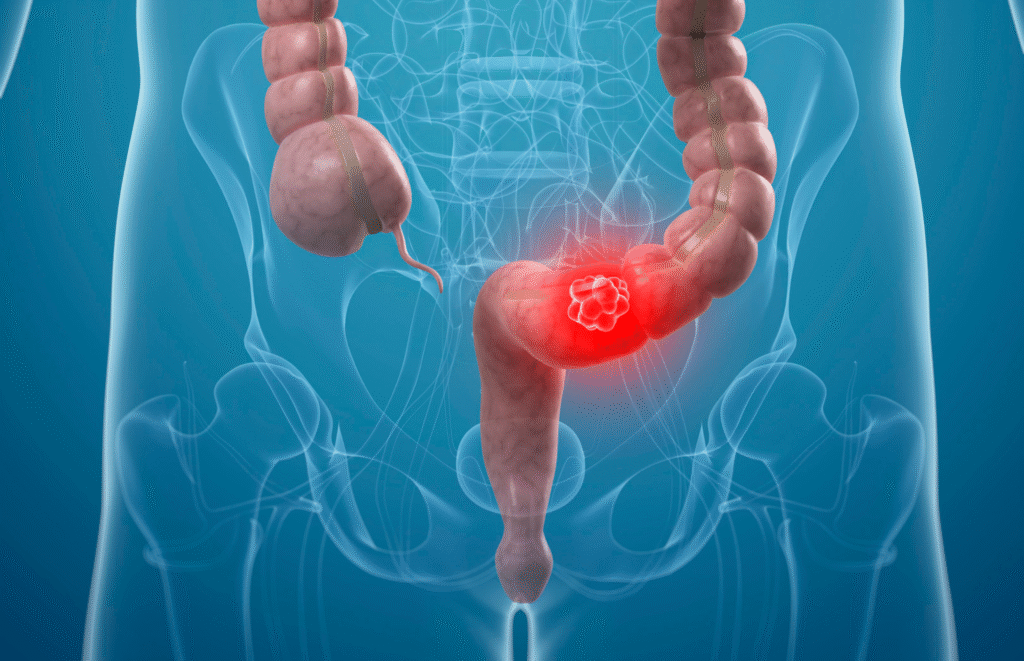
Colorectal cancer affects the colon or rectum and begins as benign growths called polyps that can turn cancerous over time. It typically develops slowly, allowing opportunities for screening and early intervention.
Risk increases with age, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic conditions like Lynch syndrome.
Key Facts:
Symptoms:
Risk Factors:
Treatment:
Prevention:
Copyright © 2025 Nurture 8 Foundation. All rights reserved.