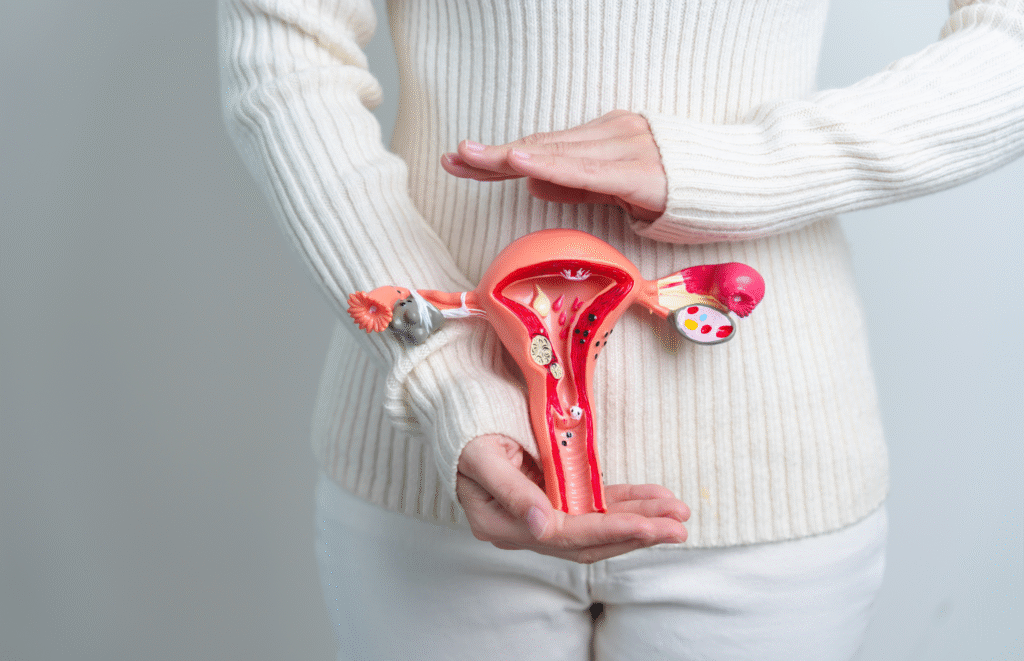
Cervical cancer begins in the cervix—the lower part of the uterus—and is almost always caused by persistent infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV). It typically develops slowly and can be prevented with regular Pap tests and HPV vaccination.
Early-stage cervical cancer rarely shows symptoms, which is why screening is crucial.
Key Facts:
Symptoms:
Risk Factors:
Treatment:
Prevention:
Copyright © 2025 Nurture 8 Foundation. All rights reserved.